What is farsightedness? Symptoms, causes & treatment
Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from farsightedness. It is more precisely a refractive defect that causes people to have trouble concentrating on close-up items while being able to see far objects well. Technically speaking, farsighted people have somewhat shorter eyeballs than average, resulting in impaired vision for things close by.
This illness may strike a person at birth, or it may develop gradually, usually with age. Numerous symptoms brought on by farsightedness might affect everyday activities and routines, therefore lowering the general quality of life. It's important to know how to manage the issue and to recognize its signs.
Indices and Causes
Especially in kids and young people, whose eyes may frequently adapt to the refractive defect, the issue may not always be obvious. However, the signs are more apparent as the eye ages and becomes less flexible. Most often reported farsightedness symptoms include:
- Focusing on near items is difficult.
- Blurry vision while writing, reading, or doing things near at hand.
- Eye pain or aching around the eyes.
- Straining the eyes or becoming somewhat tired after close-range work.
Your chances of becoming farsighted are increased genetically if your parents are. The chance may also rise with conditions including diabetes, tumors, or other eye disorders.
Care Tactics
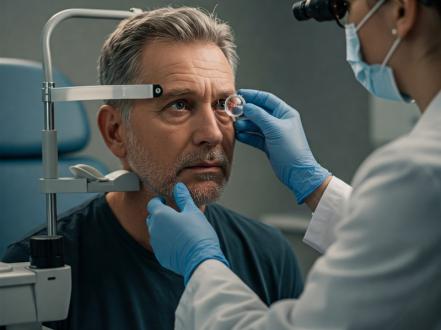
A standard eye exam that combines an eye health check with a refraction test may identify farsightedness. Using prescription contact lenses, spectacles, or certain kinds of refractive surgery, eye care specialists treat this problem.
This, nevertheless, is not an incurable illness. Anybody coping with it may go on leading a happy life without any major interruption or restriction with the appropriate care and treatment. It is thus essential to see an eye care specialist who can provide suitable guidance and treatment strategies if you believe you may have this problem.