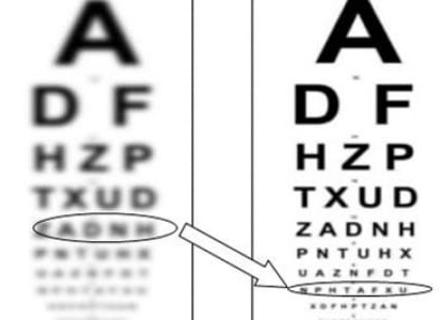
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disease characterized by thinning of the front transparent surface of the eye (cornea), changing its shape, which leads to irregular astigmatism, distortion of objects, and decreased visual acuity. The cornea of a healthy person is spherical, while in keratoconus it protrudes forward, making the cornea conical. This disrupts the path of light rays in the eye, thus distorting the image.
Causes of keratoconus
Keratoconus is a multifactorial disease. Its development is based on disruption of the structure of collagen, the shaping protein of the cornea. As a result of a decrease in collagen bonds, the cornea becomes thin and changes its shape under the effect of intraocular pressure. The role of disruption of the enzymatic balance of corneal tissues and a decrease in the level of antioxidants has also been proven. It leads to instability in the action of free radicals that cause oxidative stress.
Risk factors of keratoconus
Risk factors for the development of keratoconus include:
- Family history of keratoconus (6%-23.5%).
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet light.
- Chronic eye rubbing.
- Presence of certain diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa, Down syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, hay fever, Turner syndrome, Leber congenital amaurosis, Marfan syndrome, allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma).
Keratoconus complications
Sometimes, with the rapid progression of keratoconus, the cornea can swell significantly, resulting in severe visual impairment and scarring. It occurs when Descemet's membrane (one of the layers of the cornea) ruptures, as a result of which the intraocular fluid penetrates the corneal tissue, causing edema. This condition is called corneal hydrops and requires urgent treatment.
Symptoms of keratoconus
Keratoconus most often occurs at a young age (adolescence and age 20-30). As a rule, the process is bilateral, asymmetrical, and slowly progressive, although there is also a rapid development to a severe stage.
Keratoconus symptoms include:
- distortion of objects, double vision;
- blurred vision;
- decreased visual acuity, frequent changes of glasses or contact lenses;
- deterioration of night vision and increased distortion in poor lighting;
- sensitivity to glare and light (photophobia);
- persistent eye irritation.
In acute corneal hydrops, there are:
- sudden visual impairment;
- pain;
- red eye;
- photophobia;
- tearing.
Keratoconus diagnosis
Keratoconus can be diagnosed based on a thorough history, slit-lamp examination, retinoscopy, corneal topography (corneal curvature mapping), or optical coherence tomography (OCT) of the anterior eye segment.
Keratoconus treatment
Without optimal treatment, keratoconus can lead to vision loss.
If the symptoms are minimal and the degree of keratoconus is low, vision can be corrected with glasses or soft contact lenses.
At a more advanced stage, correction with rigid contact lenses is possible.
However, glasses or contact lenses do not solve the problem of disease progression. Therefore, in severe cases, surgical treatment is necessary. It includes:
- Corneal cross-linking is the most effective treatment, which involves cross-linking corneal collagen fibers, which strengthens inter-collagen bonds and prevents corneal reshaping;
- Intrastromal ring implantation (intrastromal keratoplasty (ICRS)) improves the structural integrity of the cornea, stopping vision loss;
- topographically guided conductive keratoplasty is a method of strengthening the cornea using radio wave energy;
- partial or complete corneal transplantation is used in the most severe cases.
Prevention
The most important thing is to detect keratoconus at an early stage. It allows achieving the maximum effect of treatment and preventing the development of complications.
Therefore, children whose parents have keratoconus are recommended regular examinations by an ophthalmologist, starting from the age of 10 (once or twice a year). It should be remembered that astigmatism is not characterized by progression, as may occur with myopia or hyperopia.
Also, relatives of a patient with keratoconus need to undergo a corneal topography test for diagnostic purposes