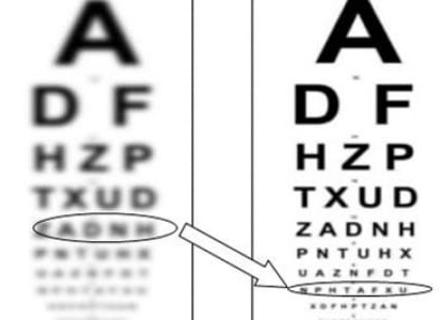
Symptoms of Amblyopia
At the first stages of development, amblyopia does not bring discomfort to the patient, so most do not know about its presence. The symptoms include:
- Frequent occurrence of headaches, especially at night;
- Fatigue after working with visual stress — working with a computer, documents, drawing, embroidery, painting;
- Coordination problems — the appearance of awkward movements;
- Squinting when looking at objects, television broadcasts, reading;
- Consideration of objects with turns and tilts of the head;
- Complaints of eye itching, redness, tearing;
- Poor eye adaptation in different lighting conditions.
Cause of Amblyopia
Risk factors for developing amblyopia include strabismus before the age of 6–8 years, conditions that contribute to deprivation. Also, amblyopia of eye can be caused by the following factors:
- prematurity;
- low weight of the newborn;
- retarded mental development;
- cerebral paralysis;
- retinopathy of prematurity;
- burdened family history regarding the presence of diseases of the organs of vision.
Treatment of Amblyopia
Based on the type of disease, the ophthalmologist selects an individual tactics for the treatment of lazy eye syndrome:
- physical training of the affected visual organ — a set of special exercises, the implementation of which allows you to return the eye to a physiologically normal position;
- elimination of provoking strabismus;
- correction of amblyopia with the help of medical optics — adequate selection of glasses, soft or hard contact lenses;
- hardware impact, in order to restore not only the coordinated work of both eyes, but also full binocular vision.
So what is amblyopia and how to prevent it?
This is a reversible functional decrease in visual acuity below the level of the age norm, which arose as a result of impaired transmission and perception of an adequate image. Preventive examinations of young children prevent the development of the disease and allow early treatment. They should be performed at 2-4 months of age or when the child reaches the age of 6-7 years.
One of the most common myths is that glasses are forever. In many cases, with amblyopia, with proper management of the child, it is possible to save him from constant spectacle dependence. With high degrees of hyperopia or astigmatism, after the cure of amblyopia, it is possible to use excimer laser correction, which makes it possible to completely rid the child of glasses.