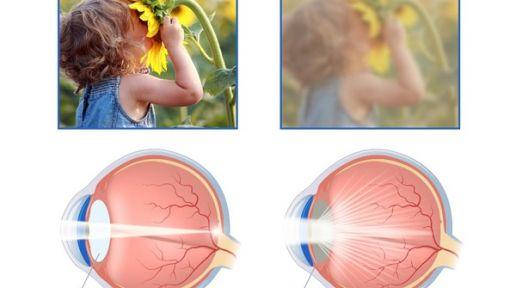
A condition called cataract is associated with irreversible changes in the lens of the eye. The disease is associated with clouding of the lens. Throughout our life, the lens is renewed with fibers. In adults, it becomes denser, loses its original transparency, which is why it lets in much less light.
What is a cataract?
It is an ophthalmic disorder characterized by partial or complete opacification of the lens of the eye, located between the iris and the vitreous humor. The lens works like an anatomical lens — it refracts rays of light and projects them onto the retina of the eye. When the lens becomes cloudy, the person's vision decreases. Cataracts lead to blindness.
Types of Cataracts
Cataract is congenital (primary) and secondary, that is, acquired. It is a fact that the percentage of the acquired form is about 97% of all cases of cataract disease, of which 90% is damage to the organs of vision in the elderly. The acquired form of the disease is divided into types:
- Traumatic cataract — occurs as a result of traumatic lesions of the organs of vision or the skull.
- Radiation of pathology — arises from the exposure of the body to excessive radiation exposure.
- The age-related — a consequence of changes in the structures of the human lens.
Do not hope that cataract will go away on its own or stop progressing. The deterioration will only continue over time and can lead to complete loss of vision.
Risk Factors of Cataracts
To date, various causes of cataracts are known that contribute to the onset of the disease. What cataracts causes can be followed:
- Age-related changes in the structure of the eye;
- Injury to the eye;
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders, vitamin deficiency);
- Pre-existing eye diseases, for example, high myopia, glaucoma;
- Toxic poisoning;
- Beam and ultraviolet irradiation;
- Increased radiation.
Among the risk factors of eye cataract are improper nutrition, smoking, alcoholism, traumas or inflammatory diseases of the eyes, the presence of cataracts of relatives of the first degree of relationship and long-term use of certain medications.
Symptoms of cataracts
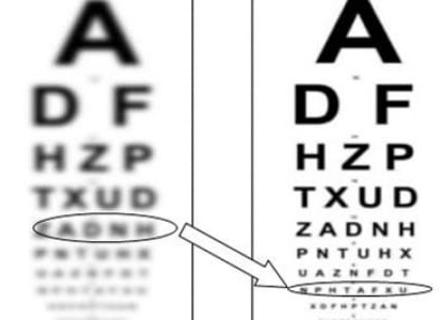
The manifestations of the disease resemble so that a person begins to see everything ‘as if in a fog’. The sensations are similar, for example, when looking through a fogged glass or through water falling from above. What are the symptoms:
- blurred, refractive vision;
- pale colors;
- dichotomy of objects or images;
- fuzzy, blurred outlines of surrounding things;
- poor visibility at night.
The mistake of many is that they believe in the myth that you can get along with cataracts without any problems. But this is not the case.
Diagnosing Cataracts
The main thing in the diagnosis of vision cataract is examination using a light (slit) lamp — biomicroscopy of the eye. Also, important are such studies as determining visual acuity, examination of the fundus, examination of visual fields, measurement of intraocular pressure.
Prevention of Cataracts
What is the prevention of the disease? Ophthalmologists quite often treat initial cataracts with special drops. These medicines contain vitamins, minerals, amino acids, ATP, antioxidants and other components that improve the metabolism of the lens tissue. But it must be borne in mind that this treatment for cataracts is not suitable for the treatment of the second and higher stage of cataract.
Most often, surgery cataracts treatment is carried out according to indications, when it becomes difficult for a person to perform his usual activities, which negatively affects the quality of his life. There are also urgent indications for which the operation must be prescribed as soon as possible.