Phacoemulsification with an intraocular lens (IOL) implantation is a safe, reliable, fast, and affordable way to restore the vision lost due to cataracts (progressive opacification of the lens). This surgery allows restoring visual function on the very day it is performed. This procedure is used to remove the natural lens not only to restore the vision but also to prevent complications in cases of combined pathologies (e.g. cataract and glaucoma).
Indications for phacoemulsification:
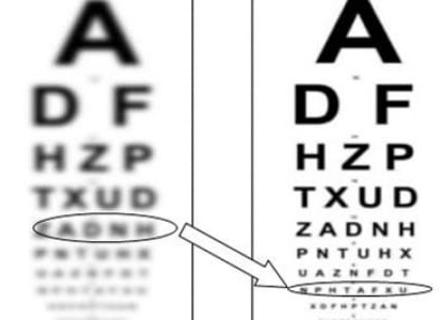
- Decrease in visual acuity by 50% or more;
- Persistent feeling of fog in front of the eyes;
- Blurred vision with color deterioration;
- Halos and glare from lamps, lanterns;
- Cloudy spots, loss of object vision.
Any type and stage of cataract is an indication for surgical intervention. Most people seek surgical treatment when the natural lens becomes too cloudy, making it difficult to perform daily activities and recognize faces. The most optimal variant is the immature stage, in which the maximum safety for the patient is guaranteed. In this situation, safety is combined with the high efficiency of phacoemulsification.
Contraindications for cataract phacoemulsification surgery:
- Infectious and inflammatory ophthalmic diseases;
- Decompensated glaucoma;
- Lack of light perception;
- Late-stage optic nerve atrophy;
- Decompensated somatic diseases (stroke or heart attack within the last 6 months, decompensated diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis (progressive course), and malignant tumors);
- Pregnancy and lactation.
Examination for cataracts
- Visometry (visual acuity testing);
- Autorefractometry;
- Measurement of intraocular pressure;
- Perimetry;
- Examination of the anterior segment of the eye;
- Examination of the ocular fundus;
- Optical coherence tomography;
- A-scan measurement and biometry (for calculation of the IOL parameters).
Preparation for phacoemulsification
Before the surgery, it is necessary to undergo a complete physical examination which includes several laboratory tests (blood and urine tests), ECG, chest X-ray, consultations with a general practitioner, ENT doctor, and a dentist. Patients with endocrine disorders (especially diabetes mellitus) require consultation with an endocrinologist. An ophthalmic surgeon should be warned about the medications you are taking.
Patients taking blood thinners should stop taking them one week before surgery due to the risk of intraocular bleeding.
The ophthalmologist may also prescribe antibiotic drops a few days before surgery to reduce the risk of infection. On the day of surgery, it is recommended to refrain from applying any cosmetics to the skin. The intake of food and liquids the day before should be limited. Before the surgery, drops are instilled into the eyes to dilate the pupils and anesthetic eye drops for local anesthesia. If necessary, sedation (administration of a relaxant to relieve anxiety and restlessness) is given.
What happens during the surgery?
Today, phacoemulsification of cataracts is an outpatient operation. This means that there is no need to stay in the hospital. On the appointed day, the patient comes to the clinic an hour before the required time, and 3-4 hours later returns home. Everything happens pretty quickly and consistently:
- The patient lies down on the operating table, the healthy eye is covered with a special napkin, and the operation area is cleaned with antiseptics;
- The surgeon makes a micro-incision in the cornea (1.8-2.2 mm) through which all further manipulations are performed;
- Viscoelastic is injected into the anterior chamber of the eye. This is a substance that protects the structures of the eye from damage;
- Then, the phacoemulsifier is inserted. This is a special ultrasonic probe that uses ultrasound to soften the cloudy lens (it breaks up the lens into small pieces), turning it into an emulsion;
- The formed substance is removed from the eye;
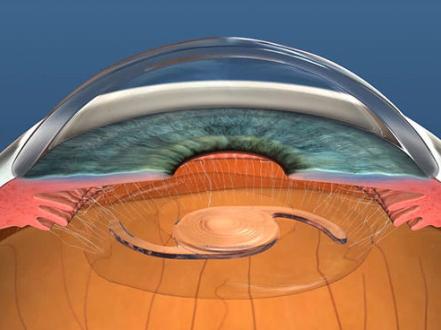
- In place of the lens, a pre-selected IOL is injected in a folded state. Thanks to the special material and design, it unfolds independently in the eye cavity and is securely fixed;
- Next, the viscoelastic is removed;
- No stitches are applied. The incision is self-sealing.
The patient is supervised by a doctor for a few hours, after which he or she can go home.
Complications
Complications of phacoemulsification are very rare and may include:
- Intraocular lens dislocation;
- Posterior capsular opacification (PCO);
- Posterior capsule rupture/vitreous loss;
- Endophthalmitis;
- Cystoid macular edema;
- Vitreous/suprachoroidal hemorrhage;
- Retinal tears or detachment.
Rehabilitation
Phacoemulsification of cataracts with an IOL implantation has a rather quick recovery period. Object vision returns immediately after the surgery, and the focus improves gradually. The most important in the rehabilitation period is the first 2 weeks after the surgery. During this period, the patient must restrict physical activity (do not lift weights) and protect the eyes from aggressive environmental factors, and also use the eye drops prescribed by the ophthalmologist. Full recovery takes 4-6 weeks on average.
Advantages of cataract treatment with ultrasound phacoemulsification
The main advantages of phacoemulsification include:
- The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis (the patient does not need hospitalization);
- The operation has a short duration (from 10 to 30 minutes on the average);
- After the operation, the patient does not lose independence and does not require any special care;
- The patient begins to see well immediately after the operation, and maximum visual acuity is restored within a few days;
- The surgery is painless and does not require stitches (the micro-incisions are sealed and heal on their own);
- The operation does not require general anesthesia and takes place under local anesthesia; it does not cause unnecessary stress on the cardiovascular system and is well tolerated by patients of any age;
- High efficiency of the surgery. Modern artificial lenses allow for maximum visual acuity, and color perception. The IOL is selected individually, taking into account the patient's profession, lifestyle and activity;
- Short rehabilitation period (in a week patients can return to work, and in a month — to lead a normal life without restrictions);
- Vision returns to 100% if its deterioration was not caused by other disorders and diseases.